In June 2003 the reports out of the United Kingdom was a name to act for people with diabetes and their physicians. In the Heart Protection Study Investigators had reported a year previous that the drug simvastatin had lowered cholesterol levels in study subjects and decrease the threat of heart attack and stroke by 25%. The scientist then looked thosesubgroup of subjects who had diabetes, and in print their conclusion in June 2003.
They found that lower levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol (often referred to as “bad” cholesterol) by 39 mg/dl resulted in a 22% fall in the possibility of a first heart attack or knock in people with diabetes. Major cardiac settlement were found even in people who entered the lessons with no symbols of main hardening and those whose LDL levels were within the ranges that don’t mechanically propose the need for LDL-lowering drugs. These results lead the researchers to terminate their statement with a statement that “statin cure should now be considered normally for all diabetic patients at suitably high risk of major vascular trial, irrespective of their initial cholesterol concentrations.”
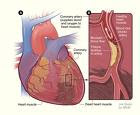
The liaison between the various forms of lipids (blood fats such as cholesterol and and heart disease was described as premature as the 1930’s and complete in the Framingham Heart Study in the 1970’s and by several other studies since then. It is a key contributor to triglycerides athroscleroses, the “hardness of the arteries” that leads to heart infection, , and PERIPHRAL VASCULAR DISEASE.
Mostly this is important to people with diabetes, in whom atherosclerosis is much more common. With diabetes Three-quarters of people will die of complications that occur from atherosclerosis. They have a 2–4 times higher risk of heart attack and stroke They also perform less well follow a heart attack or surgery. In the peripheral circulation Atherosclerosis, mostly in the leg arteries, is 2–4 times more probable in people with diabetes. This can guide to unsafe clots, sting, and amputation.
They found that lower levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol (often referred to as “bad” cholesterol) by 39 mg/dl resulted in a 22% fall in the possibility of a first heart attack or knock in people with diabetes. Major cardiac settlement were found even in people who entered the lessons with no symbols of main hardening and those whose LDL levels were within the ranges that don’t mechanically propose the need for LDL-lowering drugs. These results lead the researchers to terminate their statement with a statement that “statin cure should now be considered normally for all diabetic patients at suitably high risk of major vascular trial, irrespective of their initial cholesterol concentrations.”
The liaison between the various forms of lipids (blood fats such as cholesterol and and heart disease was described as premature as the 1930’s and complete in the Framingham Heart Study in the 1970’s and by several other studies since then. It is a key contributor to triglycerides athroscleroses, the “hardness of the arteries” that leads to heart infection, , and PERIPHRAL VASCULAR DISEASE.
Mostly this is important to people with diabetes, in whom atherosclerosis is much more common. With diabetes Three-quarters of people will die of complications that occur from atherosclerosis. They have a 2–4 times higher risk of heart attack and stroke They also perform less well follow a heart attack or surgery. In the peripheral circulation Atherosclerosis, mostly in the leg arteries, is 2–4 times more probable in people with diabetes. This can guide to unsafe clots, sting, and amputation.
No comments:
Post a Comment